5 trends shaping the future of under-roof construction
The landscape of under-roof construction is evolving rapidly, influenced by technological advancements, environmental concerns, and changing consumer preferences. As we look to the future, several key trends are emerging that are set to redefine the way we think about the spaces we live and work in. In this post, we'll explore five significant trends that are shaping the future of under-roof construction.
1. Advanced Building Materials
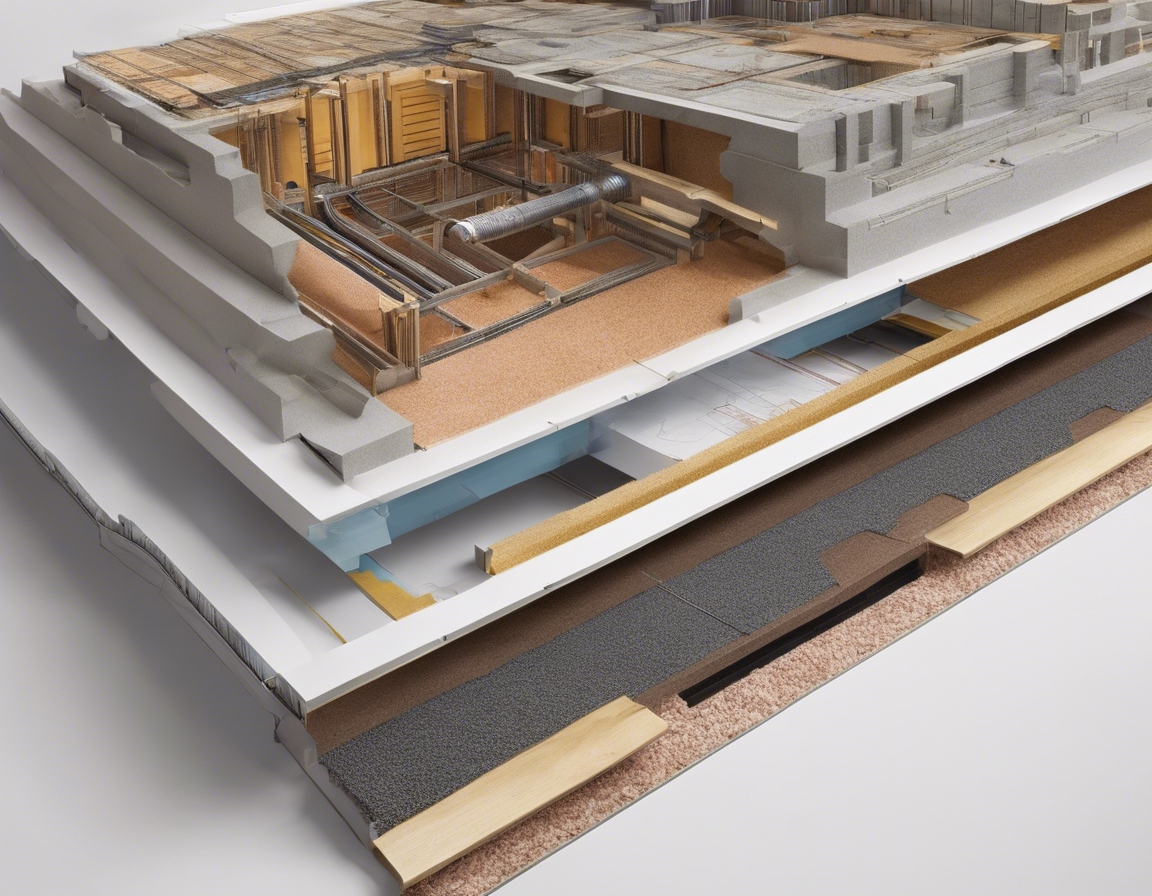
With a growing emphasis on environmental responsibility, the construction industry is seeing a surge in the use of sustainable and recycled materials. These materials not only reduce the environmental footprint of construction projects but also offer improved durability and energy efficiency.
Smart glass technology, which allows for the control of light and heat passing through windows, is becoming increasingly popular. Similarly, advanced roofing materials that reflect more sunlight and reduce heat absorption are being developed to improve energy efficiency.
Self-healing concrete, embedded with bacteria that produce limestone, can automatically repair cracks and increase the longevity of structures. This innovative material is poised to revolutionize the construction industry by reducing maintenance costs and extending the life of buildings.
2. Green Building and Sustainability
Energy efficiency remains a top priority in under-roof construction. Insulation techniques, energy-efficient appliances, and smart home systems are becoming standard practices to reduce energy consumption and lower utility bills.
Green roofs and living walls are not only aesthetically pleasing but also provide insulation, reduce stormwater runoff, and improve air quality. These features are increasingly being incorporated into urban buildings to create more sustainable and livable environments.
Water conservation is becoming a critical aspect of sustainable construction. Rainwater harvesting systems, low-flow fixtures, and water-efficient landscaping are being implemented to minimize water usage and promote sustainability.
3. Technological Innovations
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is transforming the construction process by enabling more accurate planning, design, and management of buildings. This technology facilitates better collaboration among stakeholders and can lead to more efficient and cost-effective projects.
Prefabrication and modular construction are gaining traction as they allow for faster, more efficient building processes with less waste. These methods can significantly reduce construction time and offer greater flexibility in design.
The use of automation and robotics in construction is on the rise, leading to increased precision and safety on job sites. These technologies also help address labor shortages by performing repetitive or dangerous tasks.
4. Design Trends
Open floor plans and flexible spaces are becoming increasingly popular as they allow for easy reconfiguration to accommodate changing needs. This trend reflects a shift towards more adaptable and multifunctional living environments.
Maximizing natural light is a key design trend that not only enhances the aesthetics of a space but also contributes to energy savings and occupant well-being. Large windows, skylights, and strategically placed mirrors are some of the ways to achieve this.
Smart home technology is becoming an integral part of modern construction, offering homeowners convenience, security, and energy efficiency. From automated lighting to intelligent thermostats, smart systems are being seamlessly integrated into the fabric of homes.
5. Regulatory and Safety Advances
Building codes are constantly being updated to reflect the latest safety standards and sustainability practices. These enhancements ensure that new constructions are safe, energy-efficient, and environmentally friendly.
As extreme weather events become more common, there is a growing focus on creating disaster-resilient structures. This involves using materials and design principles that can withstand natural disasters, protecting both the occupants and the investment.
Health and wellness are becoming central to construction design, with an emphasis on creating spaces that promote occupant health. This includes considerations for air quality, natural lighting, and the use of non-toxic materials.





Comments (0)