The future of sustainable living with wood
Sustainable living is a comprehensive approach that seeks to reduce an individual's or society's use of the Earth's natural resources. In the context of construction, this means creating buildings that are energy-efficient, have a minimal environmental footprint, and are made from renewable resources. Wood, as a building material, stands out for its natural origin, renewability, and capacity for carbon storage, making it a prime candidate for sustainable construction.
The demand for sustainable living spaces is on the rise as more people become aware of the environmental impacts of their lifestyle choices. Eco-conscious individuals are seeking out building solutions that align with their values of reducing carbon emissions and preserving natural habitats. This shift is driving innovation in the use of wood for construction, as it is both a traditional and a renewable material.
The Role of Wood in Sustainable Living
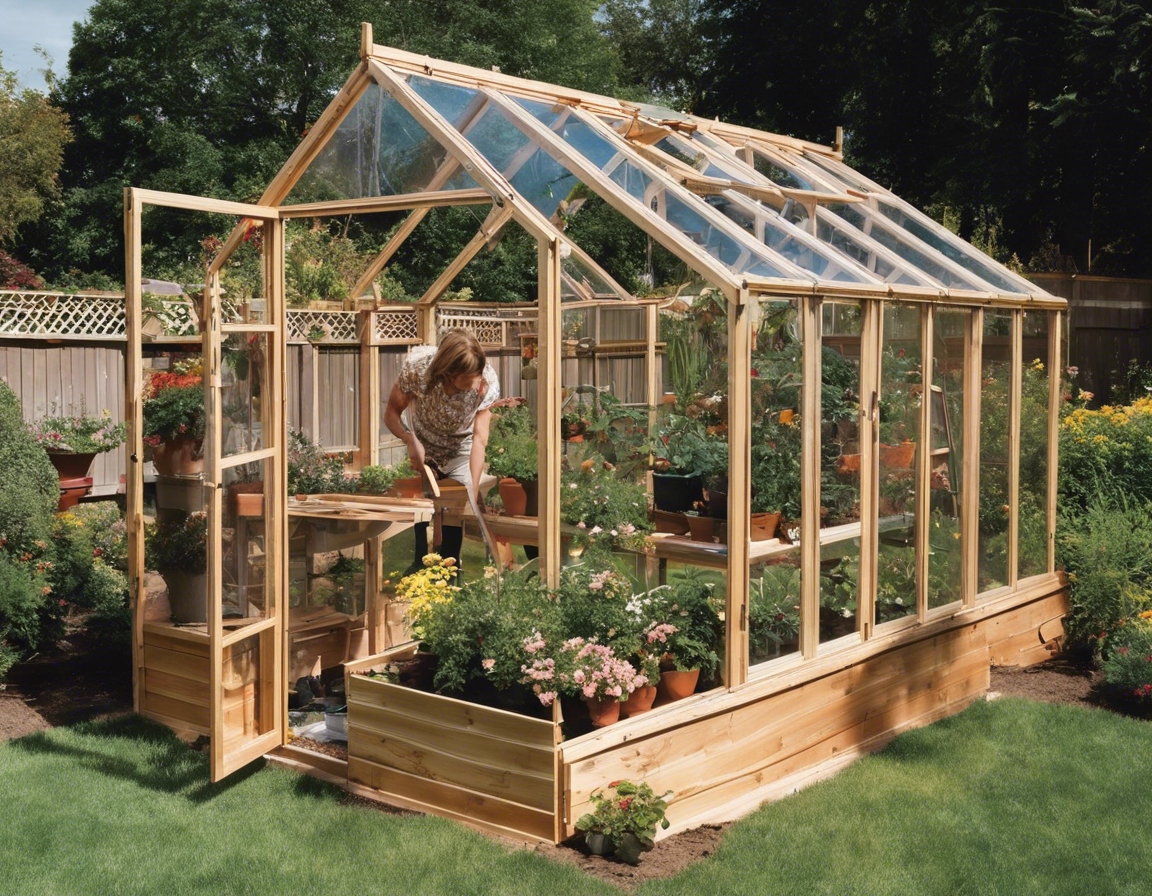
Wood is a unique building material because it is both renewable and biodegradable. Responsibly sourced wood ensures that for every tree harvested, another is planted, maintaining the balance of forest ecosystems. This cycle of growth and renewal positions wood as a sustainable choice for the future of construction.
Trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere as they grow, storing carbon in their fibers. When harvested and used as a building material, wood retains this carbon, preventing it from re-entering the atmosphere. This natural process of carbon sequestration makes wood an environmentally beneficial material in the fight against climate change.
Wood has excellent natural insulation properties, which can reduce the energy needed for heating and cooling buildings. This energy efficiency is a key component of sustainable living, as it leads to lower greenhouse gas emissions and reduced reliance on fossil fuels.
Advancements in Wood Technology
Engineered wood products, such as cross-laminated timber (CLT) and glue-laminated timber (glulam), are revolutionizing the construction industry. These products offer greater strength and durability than traditional wood, while still maintaining the environmental benefits of the material.
Advances in wood treatment technologies have extended the life of wood products, reducing the need for frequent replacement and further enhancing their sustainability. These treatments can also protect wood from pests and decay, ensuring that wooden structures can stand the test of time.
Smart wood technologies, including sensors and monitoring systems, are being integrated into wooden structures to optimize their performance and sustainability. These innovations contribute to the creation of 'living buildings' that are responsive to their environment and occupants.
Sustainable Forestry Practices
Ensuring that wood comes from sustainably managed forests is crucial for the future of sustainable living. Sustainable forestry practices include selective logging, maintaining biodiversity, and protecting water resources.
Certification systems like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) provide a way for consumers to identify wood products that have been sourced from responsibly managed forests. These standards are essential for maintaining the integrity of sustainable wood sourcing.
Agroforestry and permaculture are agricultural systems that integrate tree cultivation with crop and livestock farming. These approaches can enhance the sustainability of wood production by creating diverse ecosystems that support a variety of species and soil health.
Design Innovations with Wood
Biophilic design principles, which incorporate natural elements into the built environment, are gaining popularity. Wood plays a significant role in this design philosophy, providing a connection to nature that can improve well-being and reduce stress.
Modular construction with wood is an emerging trend that offers numerous sustainability benefits. Prefabricated wooden components can be assembled quickly on-site, reducing construction waste and minimizing the environmental impact of building.
Hybrid construction methods that combine wood with other materials, such as steel or concrete, are being developed to optimize the structural and environmental performance of buildings. These innovative approaches can leverage the best qualities of each material for a more sustainable future.
Challenges and Considerations
While wood is a sustainable material, its use must be balanced with concerns about deforestation and biodiversity loss. Sustainable living with wood requires a commitment to preserving forests and the species that inhabit them.
Climate change poses challenges to the durability of wood, with increased risks of damage from pests, diseases, and extreme weather events. Research and innovation in wood protection are essential to ensure the longevity of wooden structures in a changing climate.
The market for sustainable wood products is influenced by consumer preferences and trends. As awareness of the benefits of sustainable living grows, so does the demand for wood products that meet high environmental standards. Companies and consumers alike must stay informed and adapt to these evolving trends to support the future of sustainable living with wood.




Comments (0)